
Cloud Adoption in the Digital Healthcare Industry
The adoption of cloud computing has become a necessity for the rapidly changing healthcare industry. The list of advantages of cloud services adoption for healthcare includes, but is not limited to: real-time data processing, information exchanges about patient health history, improved cost-effectiveness, and the limitless backup possibility that saves crucial data from being lost. Still, the question emerges – can we fully trust the cloud storing such sensitive data as personal health information? There are multiple serious cloud security breaches in Internet history, and their number increases as the industry accelerates the pace of adoption. Let’s try to investigate this matter and think whether it is possible to make the usage of the cloud HIPAA compliant and ensure patient's privacy in the digital age.
Can we entrust the cloud with patient sensitive data?
Even though the cloud is a revolutionary data storage, it frequently brings serious security concerns. Innovative healthcare facilities that have already adopted cloud for data storage and processing are repeatedly accused of not paying enough attention to cybersecurity. Risks are high and the following security threats are our reality: malware, phishing and ransomware attacks, data theft, employee errors, Internet of things (IoT) insecurities, and many, many more. The good news, though, is that every such threat can be prevented and attacks can be stopped; cybersecurity specialists and ethical hackers are working through different types of cybercrimes in every area of healthcare - from healthcare application development to the creation of advanced medical wearables.
There are worries about cloud compliance with HIPAA regulations and the main cause for this is the risk of security breaches. Data architecture specialists work on the investigation and resolution of cloud-related security threats. Thomas Freise, Head of Data Architecture and Digital Technologies for Siemens states that healthcare enterprises are doing everything in their power to meet the related regulations and prioritize patient's privacy over the rest of cloud computing features. This makes us believe that there will be a time when the privacy of the data storage in the cloud won’t be an issue whatsoever. Although to achieve this goal, a healthcare institution must meet not only security demands for the data infrastructure but also physical access regulations, training of the responsible staff, access levels control, etc.
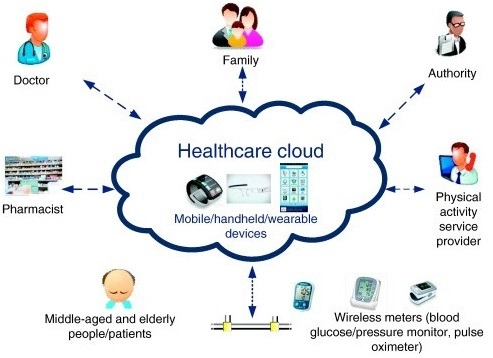
COVID-19 pandemics is currently pushing major healthcare providers to adopt cloud faster to receive patient data as soon as possible and provide appropriate care virtually, without putting clinicians and patients at risk that can be avoided with remote consultations. Electronic health records (EHR) and treatment data volumes that require quite a lot of storage already make numerous healthcare institutions adopt partial cloud architecture or hybrid cloud technology. This subdivision of the storage architecture, which will never be available in the public cloud, enables these institutions to keep certain most sensitive information parts safe and accessible.
Thus, even taking into account all risks, cloud-based storage solutions are considered to be more prospective, secure, and reliable than on-premise servers.
How cloud resources improve telemedicine?
Cloud resources can successfully optimize telemedicine when both a patient and a doctor cannot be present physically in front of each other. As one of the essential COVID-19 requirements demands social distancing and hospitals become potentially dangerous places to get the infection the parties see no other option than conversation online. As telemedicine software becomes broadly adopted by healthcare enterprises, cloud services follow them very closely: the cloud can provide the following benefits to telemedicine:
1. Streamlined data centralization. The remote doctor can observe the patient's health records and decide on the case.
2. Cost-saving. The cloud services assume less space for storing the data since physical servers are not a necessity anymore. Thus, less money and effort are needed for setting up data storage and its maintenance. Healthcare enterprises can focus the released resources on providing consulting, hiring more doctors, cybersecurity training, and so on.
3. Fast recovery. The critical data loss is not possible with cloud services. They provide formidable backups that allow telemedicine services not to be disrupted and establish continuous care for their patients.
4. Compatibility with the Internet of Things (IoT). This enables cloud services to track and report the patient's data to their physicians. As the number of wearable devices has been steadily growing over the last few years, any crucial data changes can be delivered to the medical facility through the constant updates from the cloud. Therefore, cloud services can be perceived as the heart of the telehealth industry. Its implementation is highly recommended.
What other implications of cloud services you need to consider?
Cloud services should require several additional regulations to avoid data leaks and ransomware attacks. Centralization is one of the core advantages of the cloud when the need for several devices (workstation, server, laptop, mobile device, etc.) to process the data greatly diminishes. You only need access to single centralized storage in the cloud, and it does not matter much what device you use. It simplifies access to the data, but this could be a security problem at the same time; several levels of access would resolve this issue: if only those having prioritized access can enter some specific parts of the cloud and withdraw the needed information, the rest of the staff cannot.
Public storage platforms like Dropbox do not meet HIPAA's privacy provisions, so the staff members should be trained and warned not to use any external data storage resources. Additionally, healthcare software developers should consider encrypting endpoints in their apps to avoid "islands" created by the traditional IT servers and other data storages. Lastly, to meet the HIPAA regulations, strong authentication and data transfer control need to be introduced. It is achieved via a firewall and data encryption using. These are the possible ways of delivering appropriate patient data security and privacy within the cloud.
Other potential issues of the cloud are still to be discussed and overcome, such as the processing of locally stored data by any third-party healthcare apps. The possible complication is that such apps should be able to transfer data to the cloud in a proper format and fit the cloud reports and updates. Accordingly, apart from cloud adoption as a storage alternative to the traditional IT servers, the healthcare personnel should secure any physical devices and services that are connected to the cloud to avoid data leaks while requests are being sent from the client to the data storage.
Conclusion - how to make cloud HIPAA compliant?
Conclusively, cloud services are an integral part of healthcare digitization. It’s the future of telemedicine and overall healthcare development and should be put into practice by more and more institutions. Cloud services are valuable for streamlining telemedicine services where the timely appointment might be a matter of life and death. Additionally, the cloud services save clinicians’ time as they provide a full report on the client's medical records in a matter of seconds.
The threat of ransomware and other cyberattacks remains a concern for the experts and this hampers the full implementation of cloud services in worldwide medicine. Still, the cloud developers work hard to deliver the appropriate security level to the patient's sensitive information to comply with HIPAA requirements, which serve as a safety guarantee. We dare to predict that they will succeed sooner than later. Although, a secure cloud does not make the healthcare organization HIPAA compliant and leak protected, as HIPAA compliance must be enforced on all levels of the organization, from the software they're using to, for instance, whether or not people should bring their own devices at work and whether they can use public Wi-Fi from a work laptop (spoiler: no.) There are many more steps like training staff, ensuring proper authentication, physical location admittance policies, multi-level data access, risk management, etc. If the data of your healthcare organization is in the cloud already or about to go there, please make sure you pay attention to those additional steps.
Tell us about your project
Fill out the form or contact us

Tell us about your project
Thank you
Your submission is received and we will contact you soon
Follow us
